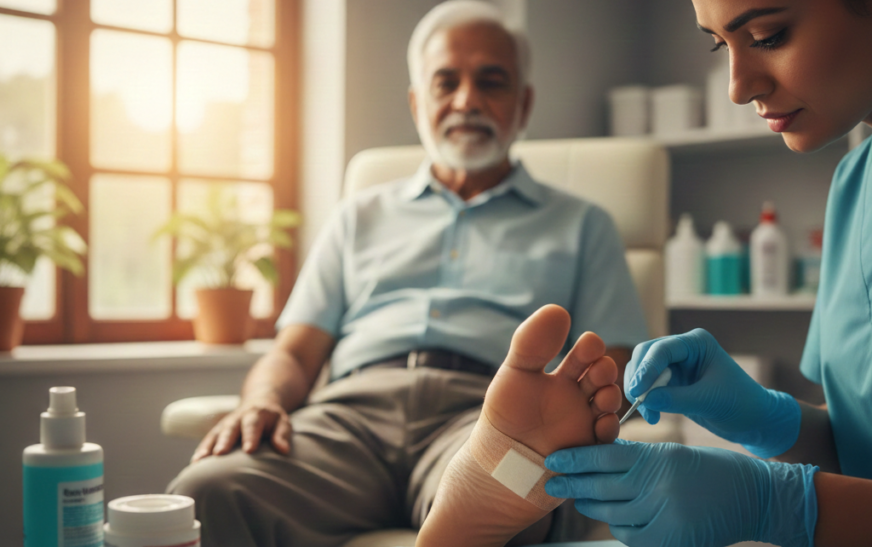
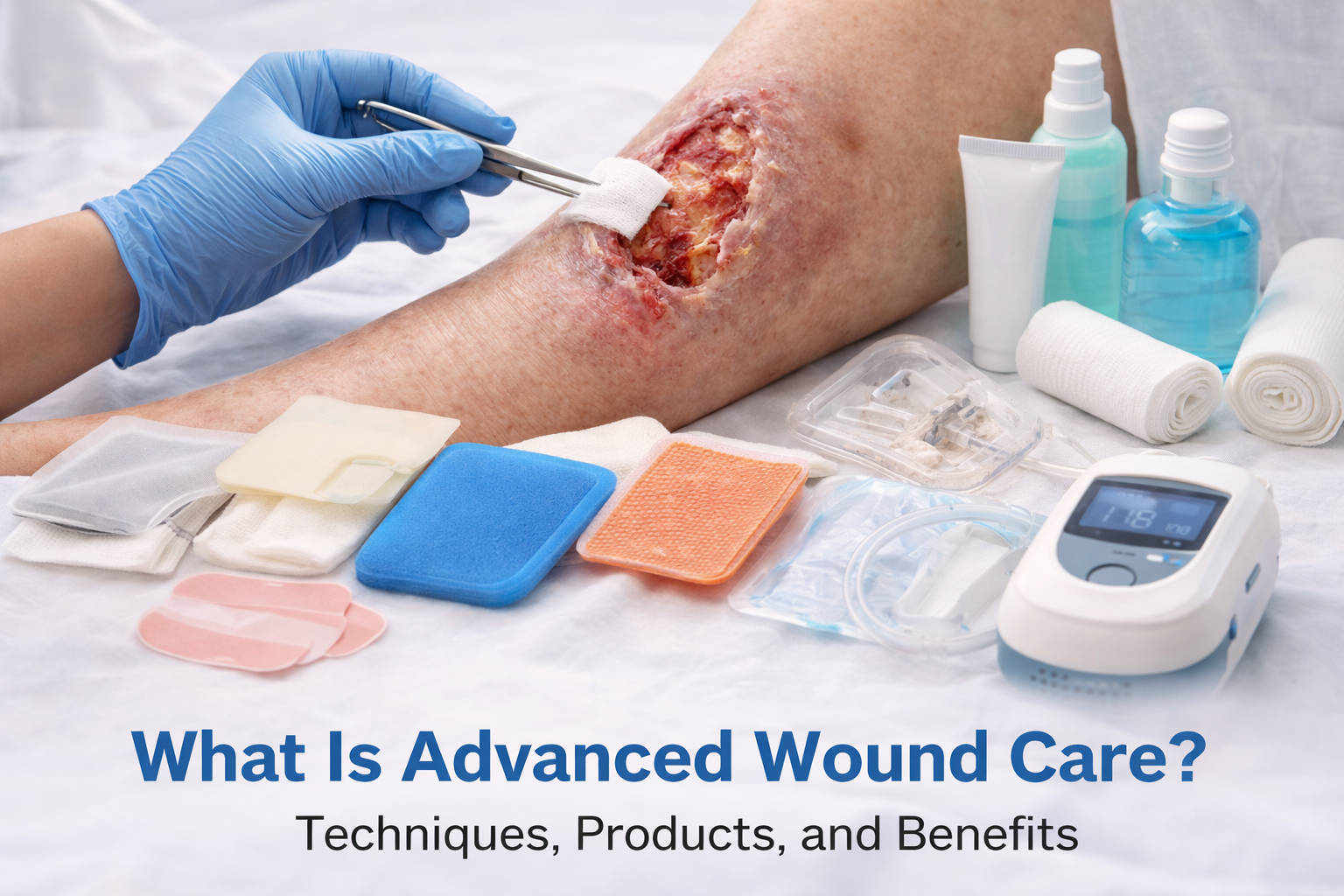
People who have diabetes often notice that their wounds are not healing quickly This is mostly seen in the feet and lower legs of an individual .Sometimes, even a small cut or bruise can turn into a serious issue if it is ignored. This happens because diabetes affects blood flow and damages the nerves. When the reasons for slow healing are understood and proper care is taken on time, many problems can be avoided. This article explains how diabetic wound care in clear and simple language. Its main focus is on the pain management, correct dressing, helping wounds heal, and preventing future wounds.
Why Do Wounds Heal Slowly in Diabetic Patients?
In diabetes, high blood sugar levels affect the body’s natural healing process. Several factors contribute to delayed wound healing:
Poor blood circulation reduces oxygen supply to the wound
Nerve damaged (diabetic neuropathy) reduces pain sensation
High sugar levels weaken the immune system
Increased risk of infection
Because of reduced sensation, many diabetic patients may not even notice a wound until it becomes severe
Common Types of Wounds in Diabetic Patients
Diabetic patients commonly experience:
Foot ulcers
Cuts and cracks on heels
Blisters from tight footwear
Surgical wounds that heal slowly
Pressure sores in bedridden patients
Among these, diabetic foot ulcers are the most serious and common.
Why Are Diabetic Wounds Painful (or Sometimes Painless)?
Pain in diabetic wounds varies from person to person.
Painful Wounds
Caused by infection or inflammation
Increased pressure or swelling
Tissue damage
Painless Wounds
Caused by nerve damage
Patients may ignore wounds unknowingly
Lack of pain does not mean the wound is harmless.
Signs of an Infected Diabetic Wound
An individual should see medication provider immediately if noticed :
Redness around the wound
Swelling around the wound
Pus or foul-smelling discharge
Increased pain
Fever
Black or dead skin around the wound
Early treatment of an individual can prevent serious complications.
Basic Wound Care for Diabetic Patients (Step-by-Step)
Clean the your hands before touching the wounded area
Clean gently with saline or clean water
Avoid harsh antiseptics unless it is advised
Dry the Area Carefully
Pat dry with clean gauze
Do not rub the wound
Apply Appropriate Dressing
Use sterile dressings
Keep the wound moist but not wet
Change dressings as advised
Protect the Wound with some cotton
Avoid pressure on the affected area
Use proper footwear or padding
Pain Management in Diabetic Wounds
Pain should never be ignored.
Ways to Reduce Pain
Keep blood sugar under control
Elevate the affected limb
Use doctor-prescribed pain relief
Avoid tight bandages
Give rest the affected area
Do not self-medicate the wound without consulting a healthcare professional.
Importance of Blood Sugar Control in Wound Healing
High blood sugar:
Slows tissue repair
Feeds bacteria
Increases the inflammation
Maintaining stable blood and sugar levels significantly improves wound healing and reduces pain.
Advanced Wound Care Options for Diabetic Patients
In non-healing or severe wounds, doctors may recommend:
Specialized wound dressings
Antibiotics should be given (oral or topical)
Debridement should be done(removal of dead tissue)
Offloading the devices (special shoes)
Regular wound assessment
These treatments should be done under the medical supervision.
Daily Foot Care Tips for Diabetic Patients
Diabetic foot wound care and infection prevention
Inspect feet daily if there any cuts or redness
Wash your feet with lukewarm water
Dry thoroughly between toes
Moisturize dry skin (avoid between toes)
Trim nails carefully
Wear comfortable footwear , closed footwear
What NOT to Do with Diabetic Wounds
Avoid these common mistakes:
Ignoring small cuts
Walking with barefoot
Using home remedies without advice
Cutting corns or calluses at home
Applying tight bandages
Delaying medical care
When Should a Diabetic Patient See a Doctor for a Wound?
Consult a doctor if:
The wound does not improve in 2–3 days
Pain increases
Signs of infection appear
There is black or dead tissue
Fever develops
Early medical intervention can save the limbs and lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (Patient-Focused)
1. Why are the diabetic feet wounds are dangerous?
Diabetic feet wounds are dangerous because of the poor circulation of blood and the nerve damage increases the infection risk and delay in healing.
2.Diabetic wounds can be healed quickly or not?
Yes, diabetic wounds can be healed quickly with early care, good controlling of sugar , and proper wound management.
3.Diabetic wounds should be kept dry or moist ?
Moist (with proper dressing) promotes faster healing.
4.Is pain always present in diabetic wounds?
No. Some wounds may be painless due to nerve damage.
Key Takeaway (Featured Snippet Optimized)
Diabetic patients are at higher risk of slow-healing and painful wounds due to the poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood and sugar levels. Proper wound cleaning, regular dressing of wounds , pain management, and strict blood and sugar control are essential to prevent infection and serious complications. Early medical care plays a crucial role in safe and effective healing of wounds .
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), people with diabetes are at higher risk of foot infections and delayed wound healing.
https://www.who.int