Wounds are a very common part of life. From a small scratch on your finger to a surgical cut or a long-lasting ulcer, wounds can happen to any individual at any age. Some wounds heal quickly without taking much care, but some wounds take a long time and need medical attention.
Understanding the types of wounds, especially the difference between the acute and the chronic wounds, is important for giving proper care, needs faster healing, and prevention should be taken . In this article, we will explain acute and chronic wounds in a simple and clear way so that even an individual without a medical background can understand easily.
What Is a Wound?
A wound is a damage or a break in the skin or the underlying tissues. It can occur due to some injury, surgery, burns, pressure, or some medical conditions.
Common Causes of Wounds are :
- Accidents or falls
- Cuts, scratches , or tears
- Surgical process
- Burns (heat, chemical, or electrical)
- Poor blood circulation of body
- Long-term illnesses such as sugar
Types of wounds
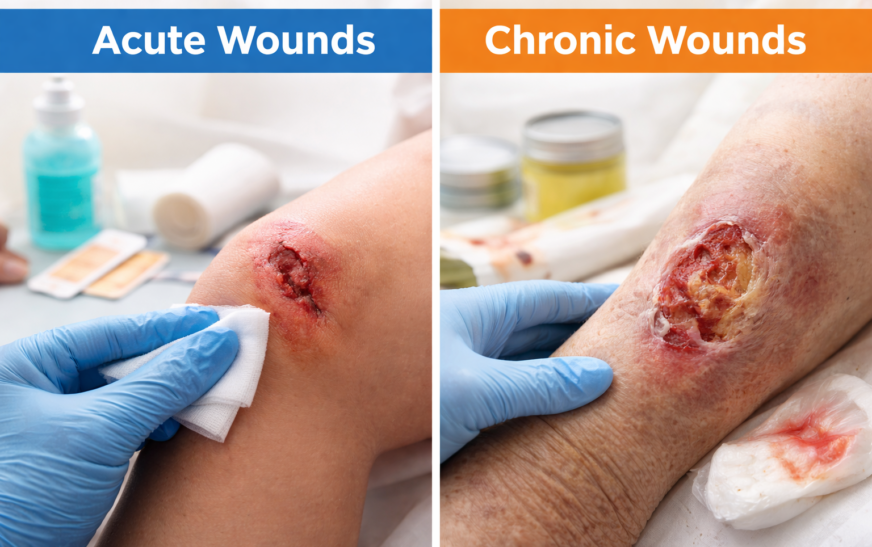
Acute Wounds
What Are Acute Wounds?
Acute wounds are the wounds that heal in an expected and timely manner, usually within a few days or within a week . These wounds follow the normal stages of healing and do not cause long-term problems to an individual. In simple words, acute wounds heal fast when proper care is taken.
Common Examples of Acute Wounds
- Cuts from the sharp objects
- Minor burns
- Scratches and abrasions
- Surgical cuts
- Stitches after surgery
How Acute Wounds Heal
Acute wounds heal through a natural and well-organized process which is called wound healing, which happens in stages.
Stages of Acute Wound Healing
1. Blood clots form in an individual to stop bleeding
- The body immediately starts protecting the wound
2. Inflammation
- Mild redness, swelling, and pain also occur
- White blood cells fight infection
3. Proliferation
- New tissue starts forming
- Skin begins to close over the wound
4. Maturation (Remodeling)
- The wound strengthens
- Scar tissue may form
Care Tips for Acute Wounds
- First Clean the wound gently with the clean water
- Keep it dry and covered
- Apply antiseptic if advised
- Change dressings regularly
- Watch for signs of infection
Chronic Wounds
What Are Chronic Wounds?
Chronic wounds are the wounds that fail to heal within the normal time period , it usually takes more than 4–6 weeks. These wounds often stop healing or heal very slowly due to health problems of an individual. In simple terms, chronic wounds are slow-healing or non-healing wounds
Common Types of Chronic Wounds
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- It usually Occur in people with diabetes
- It often Caused by poor blood flow and nerve damage
Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores)
- Develop due to prolonged pressure on the skin
- Common in bedridden or immobile patients
Venous Leg Ulcers
- Caused by poor blood circulation in the legs
- Often seen in older adults
Arterial Ulcers
- Occur due to reduced blood supply
- Usually painful and slow to heal
Symptoms of Chronic Wounds
- Wound present for weeks or months
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Swelling around the wound
- Foul-smelling discharge
- Change in wound color
- Thick or hardened wound edges
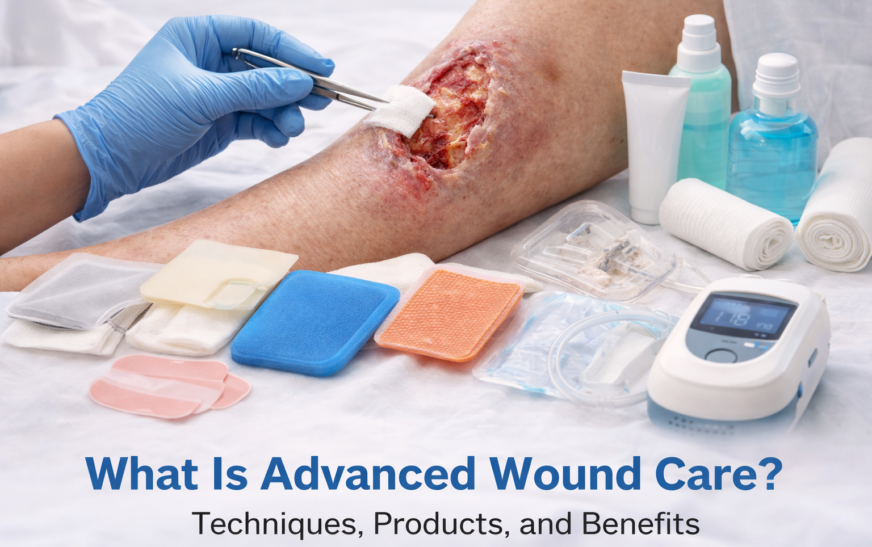
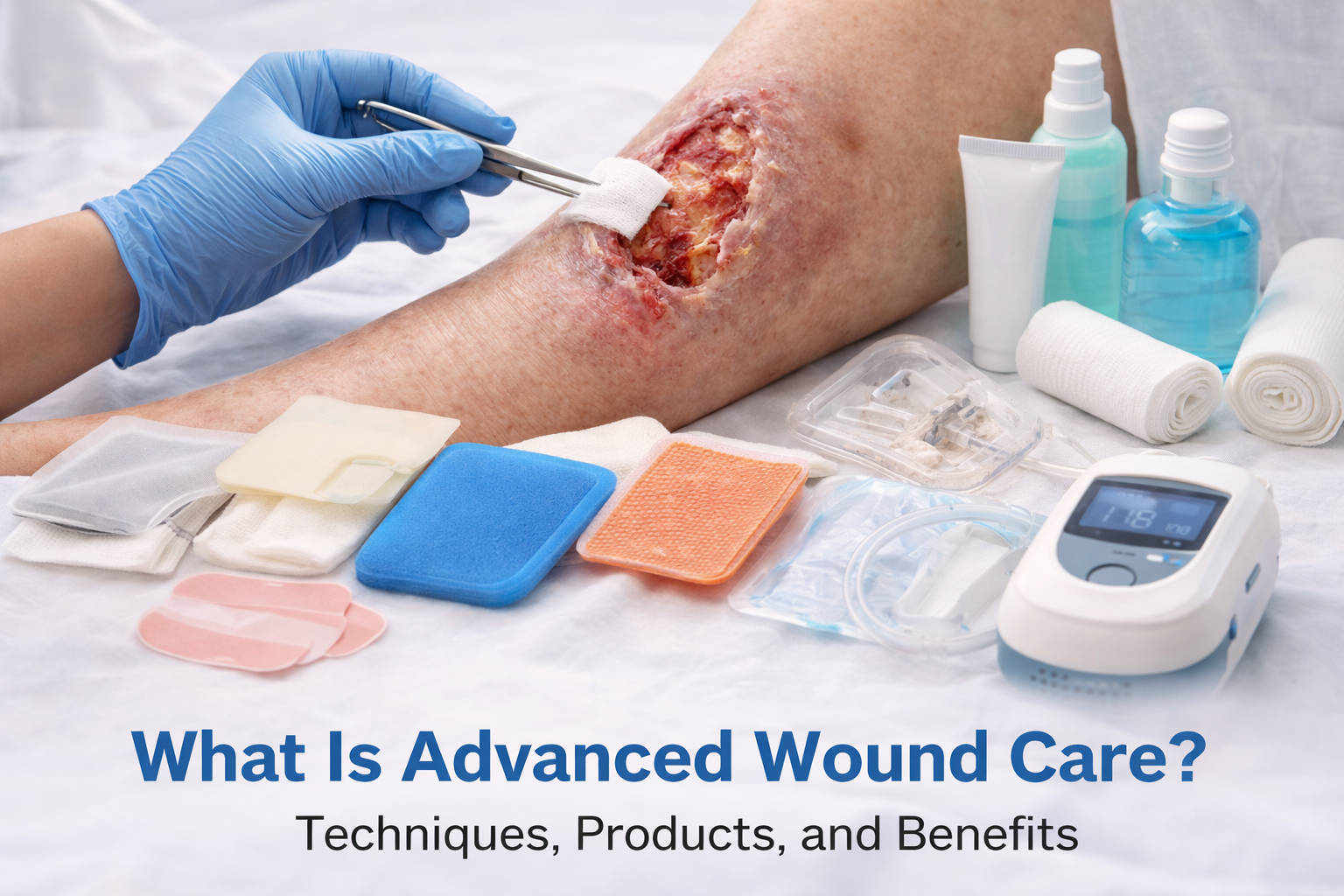
Treatment and Management of Chronic Wounds
Chronic wounds need very special medical care and long-term management.
Common Treatment Methods are :
- Regular wound cleaning and dressing
- Removing the dead tissue (debridement)
- Infection control with antibiotics
- Pressure relief techniques should be given
- Blood sugar control in diabetics
- Improved nutrition and hydration
Key Differences Between Acute and Chronic Wounds
Acute vs Chronic Wounds: Comparison Table (Explained)
Healing Time
- Acute wounds: Heal quickly (days to weeks)
- Chronic wounds: Heal slowly (months or longer)
Cause
- Acute wounds: Injury or surgery
- Chronic wounds: Underlying health conditions
Healing Process
- Acute wounds: Follow normal healing stages
- Chronic wounds: Healing process is disrupted
Risk of Infection
- Acute wounds: Low risk if cared properly
- Chronic wounds: High risk of infection
Factors That Affect Wound Healing
Physical Factors
- Age
- Blood circulation
- Oxygen supply
Medical Factors
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Immune disorders
Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking
- Poor diet
- Lack of movement
Factors Affecting Wound Healing
Healing of wounds is influenced by many factors such as age, blood circulation of the body ,oxygen supply, nutritious food , and immune strength. Medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and infections slow down the healing process.Lifestyle habits like smoking, poor eating habits , and lack of physical activity also negatively affect the healing process.
Prevention Tips for Both Acute and Chronic Wounds
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Eat a balanced, protein-rich diet
- Manage chronic conditions like diabetes
- Avoid smoking
- Move regularly to improve circulation
- Protect skin from injuries
Conclusion
Wounds may seem very simple, but they can become serious if not taken proper care . Acute wounds usually heal quickly with basic care, while chronic wounds need medical attention more and long-term management. Understanding the difference between these two types of wounds helps in early treatment, faster healing of wound and prevention of complications.
Taking care of your wound today can save you from major problems tomorrow.