Diabetes is a common health problem, but many people do not fully understand what it means or how it affects the individual’s body. This confusion may leads to fear, late diagnosis, or poor control of blood and sugar levels. This article explains diabetes in simple and easy language, so that patients and their families can easily understand what is happening inside the human body and how diabetes can be managed effectively.
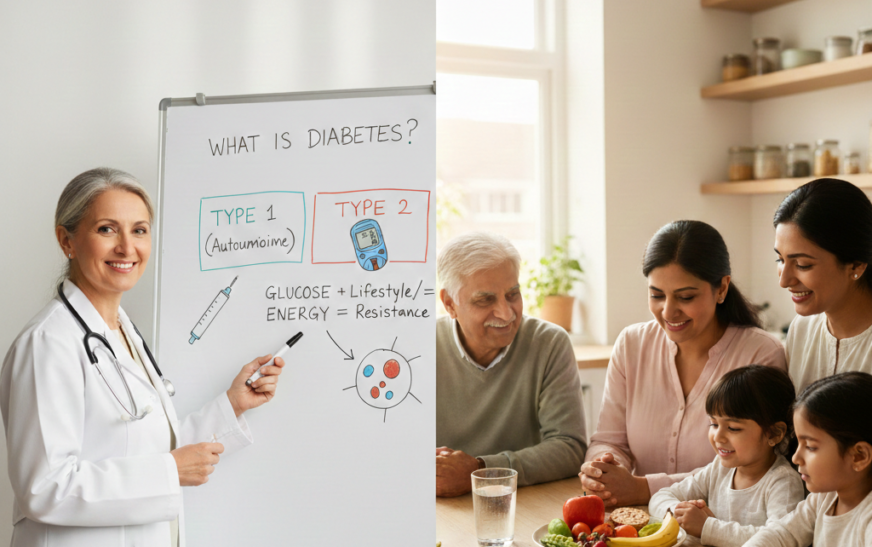
What Is Diabetes? (Simple Explanation)
Diabetes is a condition in which the level of sugar in the blood becomes higher than normal.
When we eat food, especially foods containing carbohydrates like rice, bread, fruits, or sweets, the body breaks them down into glucose (sugar). This glucose enters the bloodstream and is used by the body for energy. To move glucose from the blood into the body’s cells, the pancreas releases a hormone called insulin.
In diabetes:
The body does not make enough insulin, or
The body cannot use insulin properly
Because of this, glucose remains in the blood instead of entering the cells, causing high blood sugar levels.
Why Does the Body Need Insulin?
Insulin works like a key. It opens the door of the body’s cells so sugar can easily enter and can be used as energy. Without the enough insulin or when insulin does not work properly, glucose stays in the blood and causes diabetes.
Sugar stays in the blood
Cells do not get enough energy
The body feels tired and weak only
Over time, high blood and sugar damages organs and blood vessels.
What Are Normal and High Blood Sugar Levels?
Normal fasting blood sugar: 70–99 mg/dL
Prediabetes: 100–125 mg/dL
Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher (fasting)
Post-meal and HbA1c tests are also used to confirm diabetes and assess long-term control.
Types of Diabetes Explained Simply
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes usually begins in childhood or young adulthood. In this condition, the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. As a result, the body produces little or no insulin.
People with Type 1 diabetes:
Need insulin injections daily
Cannot control diabetes with diet alone
Require lifelong medical care
Type 1 diabetes is not caused by lifestyle habits.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. It usually develops in adults but is now increasingly seen in younger people as well.
In Type 2 diabetes:
The body produces insulin but does not use it effectively
Blood sugar levels rise slowly over time
Risk factors include:
Overweight or obesity
Lack of physical activity
Unhealthy diet
Family history
Type 2 diabetes can often be controlled with lifestyle changes, oral medicines, and sometimes insulin.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. changes reduce insulin effectiveness, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Although it usually resolves after childbirth, women with gestational diabetes have a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Many people with diabetes do not notice symptoms in the early stages. When symptoms appear, they may include:
Frequent urination
Increased thirst
Feeling very hungry even after eating
Fatigue and weakness
Blurred vision
Slow healing of cuts or wounds
Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
Sudden weight loss is more common in Type 1 diabetes.
What Causes Diabetes?
Diabetes develops due to a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, such as:
Family history of diabetes
Excess body weight
High intake of sugary and processed foods
Sedentary lifestyle
Stress and hormonal imbalance
Autoimmune response (Type 1 diabetes)
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose diabetes using the blood tests, including:
Fasting blood glucose test
Post-meal blood sugar test
HbA1c test (that shows average blood sugar over 3 months)
These tests helps in determining that whether a person has diabetes and how well it is being controlled.
Can Diabetes Be Cured?
There is currently no permanent cure for disease diabetes. However, diabetes can be successfully taken care of.
Type 1 people who are suffering from diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy
Type 2 diabetes can be controlled with good diet, regular exercise, weight management, and medication
With proper care, individual with diabetes can live healthy life longer .
How Is Diabetes Managed in Daily Life?
Healthy Eating
A balanced diet helps to maintain the blood and sugar levels stable. This includes:
Eating meals at regular schedule
Reducing glucose nd carbohydrates
Includes vegetables, grains, lean protein, and healthy fats in your meals
Physical Activity
Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels. Activities such as walking, cycling, or yoga for at least 30 minutes daily are beneficial.
Medication and Insulin
Doctors may prescribe oral medicines or insulin injections depending on the type and severity of diabetes.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring helps prevent sudden spikes or drops in blood sugar and guides treatment decisions.
Can Diabetes Be Prevented?
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of disease . It usually develops in adults but it is now increasingly seen in younger individuals as well.
In Type 2 diabetes:
The body produces insulin but does not uses it effectively
Blood sugar levels rise slowly over time
Risk factors include:
Overweight due to over eating or obesity
Lack of physical exercises
Unhealthy diet
Family history
Type 2 diabetes can be controlled with lifestyle changes, medicines, and sometimes the insulin also.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetes
Is diabetes caused by eating too much sugar?
Eating sugar alone does not cause diabetes, but long-term unhealthy eating habits can increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
Can people with diabetes eat sweets?
Yes, but in moderation and under medical guidance. Portion control is key.
Is diabetes a lifelong condition?
Type 1 diabetes is lifelong. Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be reversed in early stages with lifestyle changes.
Is diabetes dangerous?
If uncontrolled, diabetes can lead to serious complications. With proper care, these risks can be greatly reduced.
Final Thoughts
Diabetes is a controllable condition when understood correctly. Early diagnosis, healthy lifestyle choices, regular monitoring, and medical support play a vital role in preventing diabetes . By understanding how diabetes works and taking proactive steps, patients can maintain good health and quality of life