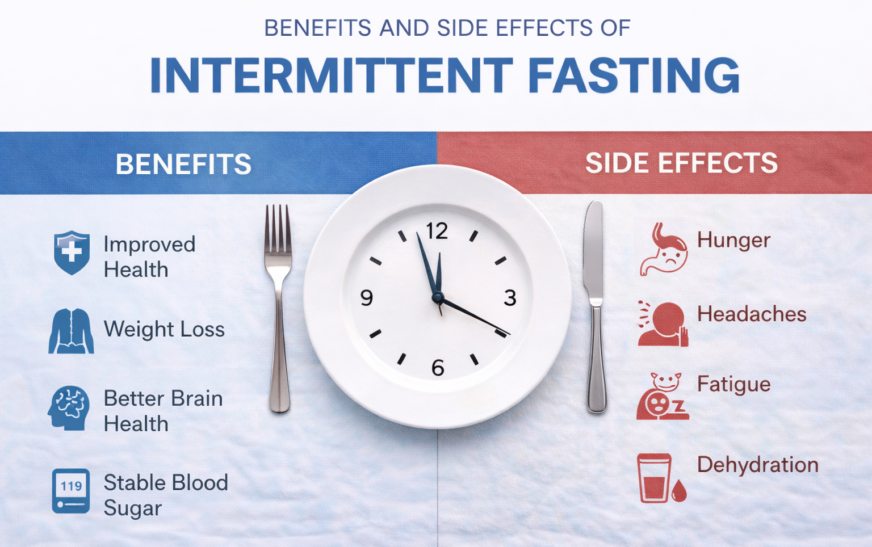
One of the most popular topics in the present wellness trends is temporary fasting. The technique mentioned above emphasises when to eat rather than what to eat. In order to give their digestive systems time to relax, people usually eat at certain times of the day and refrain from eating during the rest of the day.People who want to keep their weight under control, eat less, or feel better all over frequently engage in intermittent fasting. It might not have been considered suitable for everyone, though, as is the case with any diet plan.While some people experience benefits, others may experience drawbacks like fatigue, low energy, or trouble sleeping. Understanding intermittent fasting thoroughly is essential before starting. By considering both their own experiences and scientific evidence, people can make well-informed judgments without mindlessly adhering to trends.
Intermittent fasting: what is it?
Since intermittent starvation has become widely studied, used, and discussed, mastering the technique is essential for an intern looking into current fitness trends. Unlike regular diets, intermittent fasting emphasises timing rather than content. The potential advantages of this eating pattern, which include increased calorie intake, improved metabolism, and weight control, have generated interest.However, there may be unfavourable outcomes and drawbacks that aren’t beneficial to everyone. This essay aims to provide a clear and concise explanation for temporary hunger by eschewing technical jargon.The goal is to provide readers with accurate information to help them comprehend the topic and make decisions pertaining to their health.
Common Protocols for Intermittent fasting
Intermittent fasting participants alternate between eating and fasting. It merely instructs people on when to eat, but not whether to eat. The body may use the energy it has saved by consuming few or no calories during the hours of fasting.
Popular methods include the –
14:11 strategy : Which is simpler for novices,
16:8 strategy : Which restricts meals to one a whole day every day.
5:2 strategy : Which is eating normally for five days in a row and consuming extremely few calories on two alternate days, is another well-liked choice.
The goal of alternate-day fasting is to minimise the amount of food consumed between meals.People’s health objectives and degree of behavioural comfort have an impact on the techniques they choose.
What Effects Does Intermittent Fasting Have on the Body and Losing Weight?
Glucose, which originates from meals, is the body’s main energy source. A person’s insulin levels decrease and their body attempts to use stored fat during nutrition when they stop eating for a period of time. This change enables the body to make better use of its energy stores. Frequent fasting enhances the body’s capacity to switch between fat and carbohydrates for energy.This procedure is made easier by intermittent fasting, which prolongs the interval between meals.Cell healing is another benefit of fasting. When you fast, your body gets rid of harmful cells and makes room for better ones. This organic cleaning process increases metabolism and supports long-term well-being. The main reason why many people choose intermittent fasting is to reduce their body weight. By cutting back on meal hours, calorie intake can be naturally decreased without resorting to strict diets.Weight loss occurs gradually when the body starts using its fat stores as fuel as the fast continues. Unlike strict diets, intermittent fasting does not require the complete elimination of food categories, which makes it easier for many people to sustain over time. Intermittent fasting frequently results in gradual weight loss, which helps to avoid a sharp weight gain.Because intermittent fasting is a regular approach, many people prefer it to crash diets. The advantages, however, depend on regularity, intense exercise, and the type of food consumed during mealtimes. Methods for Lowering Insulin Levels The body can reduce its insulin levels with the use of intermittent fasting. Enzymes develop more responsive when the levels of glucose are reduced, which enhances sugar regulation.After meals, this enhanced insulin response reduces unexpected spikes in blood sugar. Those who have an increased risk for diabetes with type two may benefit most from this effect.Fasting gives the body a break from continuous digesting, which improves the way cells react to insulin. These breaks during meals can help regulate blood sugar levels and increase metabolism over time.However, results differ depending on personal health circumstances and need to be closely watched. After getting used to short-term fasting, some people report better digestion.Regular relaxation periods for the gastrointestinal system might help reduce pain and constipation.The intestines can rest during a fast instead of functioning nonstop throughout the day. Over time, this can result in better digestion and tummy comfort. However, there are individual differences in digestive responses. While some people may feel relief, others may take longer to adjust.Drink plenty of water and consume balanced meals to keep your digestive tract healthy during fasting. Intermittent Fasting and Brain Function: Boost Clarity and FocusThe body produces ketones during a fast, which provide the brain and spinal cord with an additional energy source.You may find that these ketones help you concentrate and think more properly.
Intermittent fasting helps many people focus better, think more clearly, and be more productive. Intermittent fasting can help prevent weariness that may result from eating often throughout the day . Mental energy typically appears more stable while the body changes. Good nutrition and well-planned consumption regimens are necessary for these benefits.Fasting intermittently is good for health maintenance and cell repair. A natural process which substitutes damaged cells with healthier ones is encouraged by intermittent fasting. Long-term health is enhanced and inflammation is decreased by this cellular mending. Regular fasting has been shown to slow down the aging process and lower the risk of chronic illnesses. Healthy organisms eventually protect bodily parts and operate better overall.When done properly, intermittent fasting may extend your life, however research is still ongoing.
How Nutrition Awareness and Eating Habits Are Improved by Intermittent Fasting
Fasting may affect people’s perceptions of food.Instead of being routine, meals become more deliberate and prepared. People can choose healthier diets if they know when to start and stop eating. More control over eating patterns is made possible by this methodical approach, which raises awareness of signs of fullness. Small mental adjustments can have long-term positive effects on lifestyle and eating habits.
How Nutrition Awareness and Eating Habits Are Improved by Intermittent Fasting
To Keep in mind that intermittent fasting can be challenging, especially at first. The biggest common issue appears to be increased appetite. Some people experience mood changes, headaches, and cravings. People frequently experience intense cravings for food or sweets at first. Usually, these symptoms go away as the body adapts.Individual responses differ, and some people may find intermittent fasting more difficult than others. Brief Fasting and the Development of the Brain: Boost Clarity and Focus The body produces ketones during a fast, which provide the nervous system with an alternative source of energy.These ketones can help you focus and think more clearly. Intermittent fasting helps many people focus better, think more clearly, and be more productive.Intermittent fasting could help prevent energy issues that could arise from eating frequently during the day. Mental focus typically appears more stable when the body adapts. Good nutrition and regular eating habits are necessary for these effects. For long-term health and cell repair, intermittent fasting is advantageous. A natural process that replaces damaged cells with healthier ones is encouraged by intermittent fasting. Long-term health is enhanced and inflammation is decreased by this cellular mending.Regular fasting has been shown to slow down the aging process and lower the risk of chronic illnesses. Healthy organisms eventually protect bodily parts and operate better overall.When done properly, intermittent fasting may extend your life, however research is still ongoing. How Nutrition Awareness and Eating Habits Are Improved by Intermittent Fasting may affect people’s perceptions of food. Instead of being regular, meals are now more deliberate and planned. Making better dietary decisions is made possible by understanding when to start and stop eating. Greater control over eating patterns is made possible by this methodical approach, which raises awareness of satiety and fullness signals. Small mental changes can have long-term favourable consequences on lifestyle and diet. Intermittent Fasting: Challenges and Hazards to Watch It may be challenging to fast intermittently, especially at first.Increased hunger is an especially widespread problem. Some people experience mood changes, headaches, and cravings. People frequently experience intense cravings for food or sweets at first.Once the body gets used to the following signs normally fade. Individual reactions vary, and specific individuals may have trouble more than others with fasting for an extended period.
INTERMITTENT FASTING SAFETY TIPS
When fasting, some individuals experience exhaustion or weakness, especially if their consumption of calories is excessively low. Inadequate nutrition during mealtimes may exacerbate low energy consumption levels.Furthermore, dehydration is the leading cause of dizziness. During a fast, consuming less water may lower blood pressure and cause dizziness. Drinking plenty of water and eating nutritious meals might help to alleviate these symptoms and make fasting more comfortable.Not everyone can safely undertake intermittent fasting. Some people, especially those who are dealing with health issues, require medical guidance first. It can be harmful to pregnant women. Fasting might be dangerous for certain people because it causes low blood sugar levels.It may not benefit older people who are struggling that mitigates weight. Prioritise your personal health prior to initiating any alterations. Breastfeeding mothers and expecting mothers. Giving a baby mother’s milk through their body. Periodic fasting does not imply missing food; rather, it changes our viewpoint on eating. When done correctly, the body may respond with more energy, better focus, weight loss, and a more effective metabolism.
CONCLUSION
Intermittent fasting is a lifestyle philosophy that emphasises eating habits above food limitations. When done correctly, it can provide a variety of health upsides, including weight loss, improved metabolism, increased mental clarity, and greater cellular repair. However, it has not been without risks, particularly during the adaption phase. Before beginning intermittent fasting, you must understand both the benefits and the risks. What performs well for one individual might not work for someone else. Thus, a personalised balancing strategy is essential.Intermittent fasting is an important topic of research for interns and health advocates alike, reflecting the growing trend toward thoughtful and sustainable health habits.Individuals who practice responsible intermittent fasting and pay attention to their bodies’ demands have the ability to improve the way they feel while remaining a healthy connection with food.